Conceptual physics chapter 28 reflection and refraction answers – Delve into the captivating world of optics with Conceptual Physics Chapter 28: Reflection and Refraction Answers, a comprehensive guide to understanding the fundamental principles that govern the behavior of light. Prepare to unravel the mysteries of reflection, refraction, and their countless applications in various scientific and technological fields.
As we embark on this journey of discovery, we will explore the concepts of reflection and its laws, unraveling the fascinating world of specular and diffuse reflections. We will delve into the intricacies of refraction, examining how light interacts with different media and the factors that influence its path.
Furthermore, we will uncover the remarkable phenomenon of total internal reflection and its applications in fiber optics and prisms.
1. Reflection

Reflection refers to the phenomenon where light waves bounce off a surface and return in a different direction. It is governed by the laws of reflection, which state that the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the surface at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane, and the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence.
There are two main types of reflection: specular reflection and diffuse reflection. Specular reflection occurs when light is reflected from a smooth, shiny surface, such as a mirror, resulting in a clear and sharp image. Diffuse reflection, on the other hand, occurs when light is reflected from a rough or uneven surface, scattering the light in multiple directions and producing a hazy or blurred image.
Reflection has numerous applications in everyday life, including the use of mirrors, telescopes, and microscopes. It is also used in traffic signs, safety vests, and reflective clothing to enhance visibility and safety.
2. Refraction
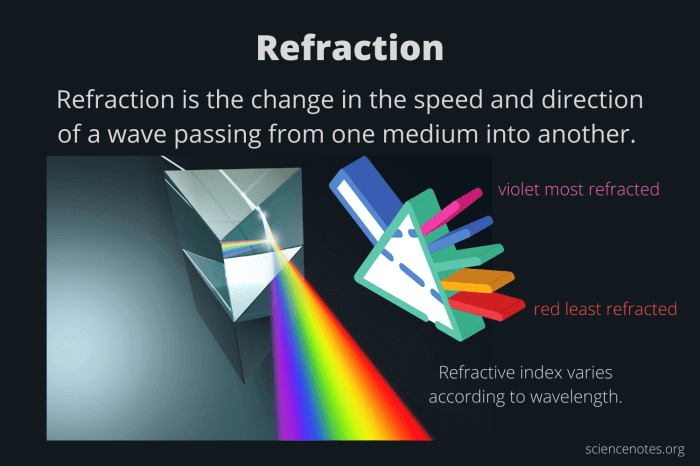
Refraction is the phenomenon where light waves change direction when passing from one medium to another with a different refractive index. The refractive index of a medium is a measure of how much light bends when passing through it.
The angle of refraction depends on the angle of incidence, the wavelength of light, and the refractive indices of the two media. As light enters a medium with a higher refractive index, it bends towards the normal, while it bends away from the normal when entering a medium with a lower refractive index.
Refraction has various applications, including the use of lenses, prisms, and optical fibers. It is also responsible for the bending of light as it passes through the atmosphere, causing stars to appear higher in the sky than they actually are.
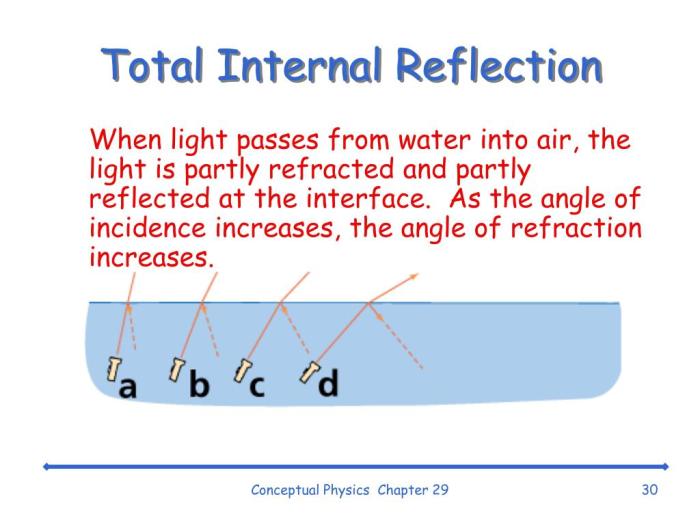
3. Total Internal Reflection
Total internal reflection is a phenomenon that occurs when light traveling in a medium with a higher refractive index strikes a boundary with a medium with a lower refractive index at an angle greater than the critical angle. In this case, all of the light is reflected back into the higher refractive index medium.
Total internal reflection has important applications in fiber optics, where light is transmitted over long distances through thin, flexible fibers by repeated total internal reflections. It is also used in prisms to create special effects and in some types of telescopes.
4. Lenses
Lenses are optical devices that focus or disperse light waves. There are two main types of lenses: convex lenses and concave lenses.
Convex lenses, also known as converging lenses, cause light rays to converge or meet at a point after passing through the lens. They are used in magnifying glasses, cameras, and telescopes to create magnified images.
Concave lenses, also known as diverging lenses, cause light rays to diverge or spread out after passing through the lens. They are used in eyeglasses to correct nearsightedness and in some types of projectors.
5. Optical Instruments
Optical instruments are devices that use lenses, mirrors, and other optical components to create images or manipulate light. Some common optical instruments include microscopes, telescopes, and cameras.
Microscopes are used to magnify small objects, allowing us to see details that are not visible to the naked eye. Telescopes are used to observe distant objects, such as stars and planets. Cameras are used to capture and record images.
Each type of optical instrument has its own unique design and purpose, but they all rely on the principles of reflection and refraction to create images or manipulate light.
6. Applications of Reflection and Refraction: Conceptual Physics Chapter 28 Reflection And Refraction Answers
Reflection and refraction have a wide range of applications in various fields, including medicine, engineering, and telecommunications.
In medicine, reflection is used in endoscopes to visualize internal organs and tissues. Refraction is used in eyeglasses and contact lenses to correct vision problems.
In engineering, reflection is used in radar systems to detect objects. Refraction is used in prisms to split light into its component colors and in lenses to focus light in optical instruments.
In telecommunications, reflection is used in fiber optics to transmit light signals over long distances. Refraction is used in lenses to focus light in optical fiber connectors.
Key Questions Answered
What is the law of reflection?
The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
What are the different types of reflection?
The two main types of reflection are specular reflection and diffuse reflection.
What is refraction?
Refraction is the bending of light as it passes from one medium to another.
What are the factors that affect refraction?
The factors that affect refraction include the angle of incidence, the wavelength of light, and the refractive index of the medium.
What are some applications of total internal reflection?
Total internal reflection is used in a variety of applications, including fiber optics and prisms.