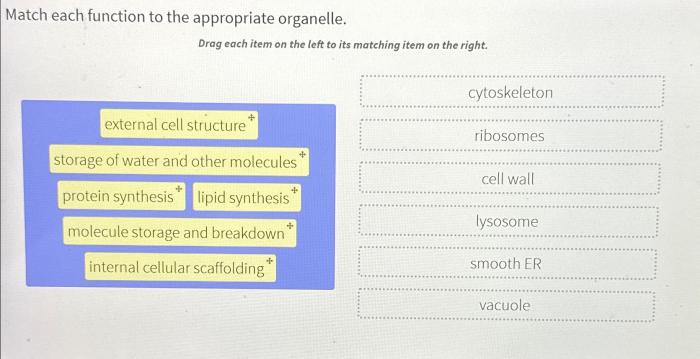
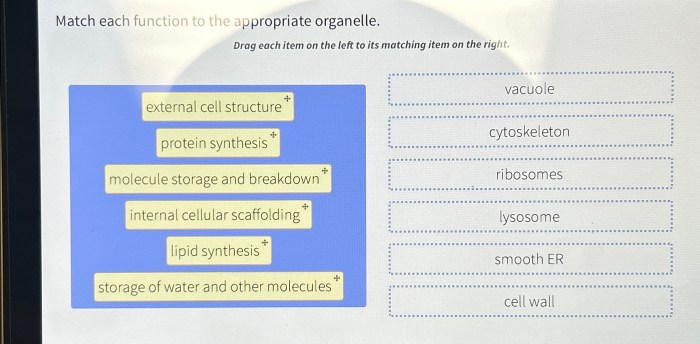
Match each function to the appropriate organelle – Delving into the fascinating realm of cellular biology, this comprehensive guide embarks on an exploration of the intricate relationship between organelle function and cellular processes. Unraveling the mysteries of the cell, we will meticulously match each vital function to its corresponding organelle, providing a profound understanding of the harmonious symphony that sustains life.
From the cell membrane’s gatekeeping role to the nucleus’s genetic control center, from the ribosomes’ protein synthesis machinery to the mitochondria’s energy-generating powerhouse, each organelle plays a pivotal role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and ensuring the seamless execution of life’s essential processes.
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a thin, flexible layer that surrounds and protects the cell. It regulates the passage of materials into and out of the cell.
Structure and Composition
- Bilayer of phospholipids with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails
- Embedded proteins that facilitate transport, signaling, and cell adhesion
- Carbohydrates attached to proteins or lipids (glycoproteins and glycolipids)
Process, Match each function to the appropriate organelle
Diffusion: Movement of molecules across the membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
Nucleus
The nucleus is the control center of the cell, containing the cell’s genetic material.
Structure
- Nuclear envelope: Double membrane with nuclear pores
- Nucleolus: Site of ribosome synthesis
- Chromatin: DNA and proteins
Process, Match each function to the appropriate organelle
Transcription: Synthesis of RNA from DNA
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are cellular organelles that synthesize proteins.
Structure
- Small and large subunits made of ribosomal RNA and proteins
- Found in the cytoplasm and attached to the endoplasmic reticulum
Process, Match each function to the appropriate organelle
Translation: Synthesis of proteins from mRNA
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes that folds and transports proteins.
Structure
- Rough ER: Studded with ribosomes
- Smooth ER: Lacks ribosomes
Process, Match each function to the appropriate organelle
Protein folding and transport
Golgi Apparatus

The Golgi apparatus is a stack of flattened membranes that modifies and packages proteins.
Structure
- Cisternae: Flattened sacs
- Vesicles: Transport vesicles
Process, Match each function to the appropriate organelle
Protein modification and secretion
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles that contain hydrolytic enzymes.
Structure
- Lysosomal membrane: Single membrane with a proton pump
- Hydrolytic enzymes: Break down macromolecules
Process, Match each function to the appropriate organelle
Intracellular digestion
Mitochondria: Match Each Function To The Appropriate Organelle
Mitochondria are organelles that produce energy for the cell.
Structure
- Outer and inner membranes
- Cristae: Folds in the inner membrane
- Matrix: Contains mitochondrial DNA and ribosomes
Process, Match each function to the appropriate organelle
Cellular respiration: Production of ATP
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells that perform photosynthesis.
Structure
- Thylakoid membranes: Stacked membranes containing chlorophyll
- Stroma: Fluid-filled space
Process, Match each function to the appropriate organelle
Photosynthesis: Conversion of light energy into chemical energy
Vacuoles

Vacuoles are membrane-bound sacs that store materials.
Structure
- Vacuolar membrane: Single membrane
- Contents: Water, ions, proteins, and other molecules
Process, Match each function to the appropriate organelle
Storage of materials
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the fluid-filled space inside the cell membrane.
Composition
- Cytosol: Aqueous solution containing ions, proteins, and other molecules
- Cytoskeleton: Network of protein fibers that provides structural support
- Organelles: Various cellular structures
Process, Match each function to the appropriate organelle
Metabolic reactions, transport of materials, and cellular movement
Quick FAQs
What is the primary function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane regulates the passage of materials into and out of the cell, maintaining the cell’s internal environment and protecting it from its surroundings.
What organelle is responsible for protein synthesis?
Ribosomes, found in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum, are the cellular machinery responsible for protein synthesis.
Where does cellular respiration occur?
Cellular respiration, the process of generating energy for the cell, takes place within the mitochondria, the cell’s powerhouses.