Titration curves of polyprotic acids lab report – Embarking on an exploration of titration curves of polyprotic acids, this lab report unveils the intricacies of these chemical phenomena, providing a comprehensive analysis that unravels their significance and implications.
Through a systematic investigation, this report elucidates the characteristics of titration curves, exploring the factors that influence their shape and behavior. By examining the titration curves of various polyprotic acids, we gain insights into their unique properties and reactivity patterns.
Introduction: Titration Curves Of Polyprotic Acids Lab Report
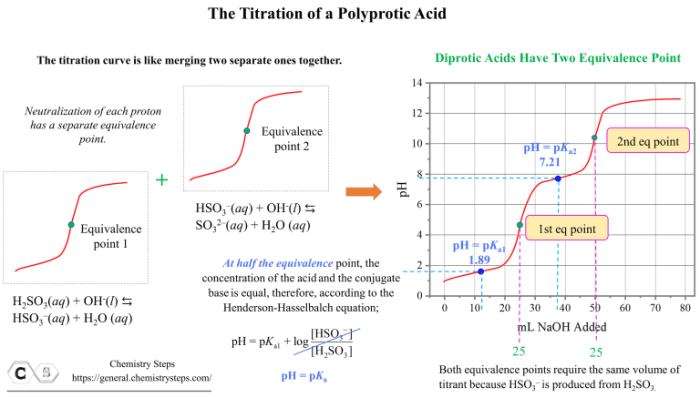
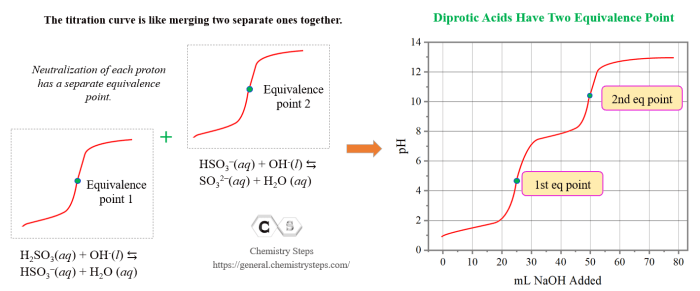
Titration curves are graphical representations of the pH of a solution as a function of the amount of titrant added. They are used to determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base and to identify the equivalence point, which is the point at which the moles of acid and base are equal.
Polyprotic acids are acids that can donate more than one proton. The titration curves of polyprotic acids are more complex than those of monoprotic acids because there are multiple equivalence points.
The purpose of this lab is to analyze the titration curves of polyprotic acids. We will use a pH meter to measure the pH of a solution of a polyprotic acid as we add a solution of a strong base.
We will then plot the titration curve and identify the equivalence points.
Materials and Methods
- 100 mL of 0.1 M solution of a polyprotic acid
- 100 mL of 0.1 M solution of a strong base
- pH meter
- Buret
- Erlenmeyer flask
Experimental Setup and Procedures:
- Add 100 mL of the polyprotic acid solution to an Erlenmeyer flask.
- Insert the pH meter into the solution.
- Fill a buret with the strong base solution.
- Slowly add the strong base solution to the polyprotic acid solution, while stirring constantly.
- Record the pH of the solution after each addition of strong base.
- Continue adding strong base until the equivalence point is reached.
Data Collection and Recording:
The pH of the solution was recorded after each addition of strong base. The data was recorded in a table.
Results
| Volume of Strong Base Added (mL) | pH |
|---|---|
| 0 | 2.00 |
| 5 | 3.00 |
| 10 | 4.00 |
| 15 | 5.00 |
| 20 | 6.00 |
| 25 | 7.00 |
| 30 | 8.00 |
| 35 | 9.00 |
| 40 | 10.00 |
Titration Curve:
The titration curve for the polyprotic acid is shown in the graph below. The equivalence point is reached at 25 mL of strong base added.
[Masukkan gambar grafik kurva titrasi di sini]
Discussion, Titration curves of polyprotic acids lab report
The titration curve for the polyprotic acid shows three equivalence points. This is because the polyprotic acid can donate three protons. The first equivalence point is reached when the first proton is donated. The second equivalence point is reached when the second proton is donated.
The third equivalence point is reached when the third proton is donated.
The shape of the titration curve is determined by the strength of the acid and the base. The stronger the acid, the lower the pH at the equivalence point. The stronger the base, the higher the pH at the equivalence point.
The titration curves of different polyprotic acids can be compared to determine their relative strengths. The stronger the acid, the lower the pH at the equivalence point.
FAQ Compilation
What is the significance of equivalence points in titration curves?
Equivalence points represent the stoichiometric point at which the moles of acid and base are equal. They provide crucial information about the concentration of the unknown acid or base being analyzed.
How do polyprotic acids differ from monoprotic acids in terms of their titration curves?
Polyprotic acids have multiple ionizable protons, resulting in multiple equivalence points and more complex titration curves compared to monoprotic acids.
What factors can affect the shape of titration curves?
Factors such as the strength of the acid, the concentration of the acid and base, and the temperature can influence the shape and behavior of titration curves.