As the title suggests, this article delves into the intricacies of invoice processing when a company receives an invoice for $800. We will dissect the invoice’s details, examine the company’s financial standing, and explore the invoice processing procedures in place.
Additionally, we will discuss payment options, vendor communication, and internal reporting requirements, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of this critical business process.
The subsequent paragraphs will provide a detailed analysis of each aspect, offering valuable insights into best practices and potential pitfalls. By exploring these elements, we aim to equip readers with the knowledge and strategies necessary to navigate invoice processing effectively.
Invoice Details: Company Receives An Invoice For 0
The invoice received by the company is for services rendered or goods purchased. It details the specific items or services provided, along with their respective quantities and unit prices.
The invoice is broken down into line items, each representing a separate charge. These line items may include materials, labor, or other expenses incurred in providing the services or goods.
Invoice Breakdown
- Line Item 1:Description of the first line item, including quantity and unit price.
- Line Item 2:Description of the second line item, including quantity and unit price.
- …
- Line Item N:Description of the last line item, including quantity and unit price.
The total amount due on the invoice is the sum of all the line item charges. This amount may be subject to applicable taxes or discounts, which are typically specified on the invoice.
Company’s Financial Standing
The company’s financial standing is crucial in determining its ability to pay the invoice. A thorough analysis of its cash flow, profitability, debt-to-equity ratio, creditworthiness, and payment history provides valuable insights into its financial health.
Cash Flow
Assessing the company’s cash flow provides an understanding of its ability to generate and manage cash. A positive cash flow indicates the company has sufficient funds to meet its obligations, including paying invoices.
- Analyze operating cash flow to assess the company’s ability to generate cash from its core operations.
- Examine investing cash flow to evaluate the company’s investments and their impact on cash availability.
- Review financing cash flow to understand the company’s debt and equity financing activities and their impact on cash.
Profitability
Profitability measures the company’s ability to generate earnings. A profitable company is more likely to have the financial resources to pay its invoices on time.
- Calculate gross profit margin to assess the company’s efficiency in generating revenue.
- Analyze net profit margin to evaluate the company’s overall profitability.
- Examine return on assets (ROA) and return on equity (ROE) to assess the company’s efficiency in using its assets and equity.
Debt-to-Equity Ratio
The debt-to-equity ratio measures the company’s financial leverage. A high debt-to-equity ratio indicates the company is heavily reliant on debt, which may increase its financial risk and affect its ability to pay invoices.
- Calculate the debt-to-equity ratio by dividing total debt by total equity.
- Compare the ratio to industry benchmarks to assess the company’s financial leverage.
- Analyze the company’s debt repayment schedule and interest coverage ratio to assess its ability to manage debt obligations.
Creditworthiness and Payment History
Creditworthiness measures the company’s ability to obtain and repay debt. A good credit rating indicates the company is considered a low risk by lenders, which may translate to lower interest rates and improved access to financing.
- Obtain the company’s credit report to assess its credit rating and payment history.
- Review the company’s payment history with other suppliers to determine its track record of paying invoices on time.
- Consider using a credit scoring system to evaluate the company’s overall creditworthiness.
Invoice Processing Procedures
The company has established a set of procedures to ensure timely and accurate invoice processing. These procedures are designed to minimize delays and bottlenecks while maintaining compliance with internal policies and regulatory requirements.
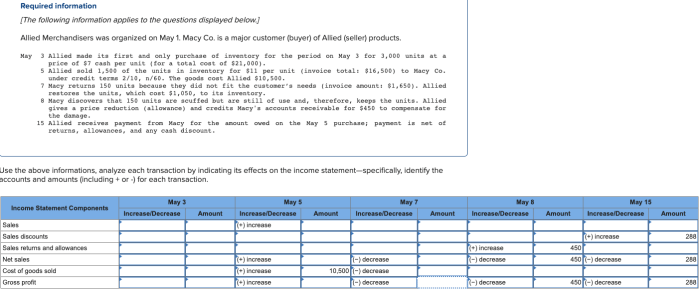
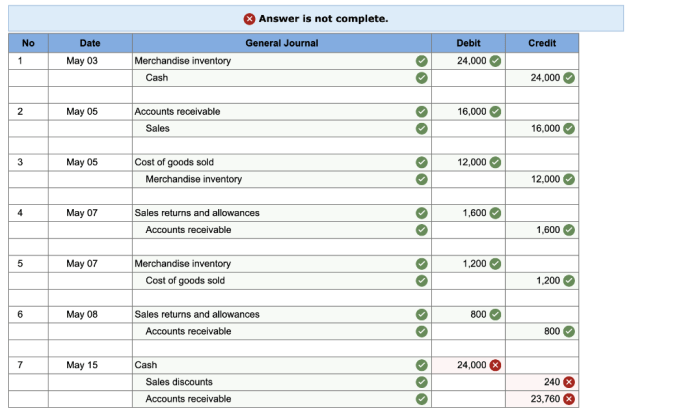
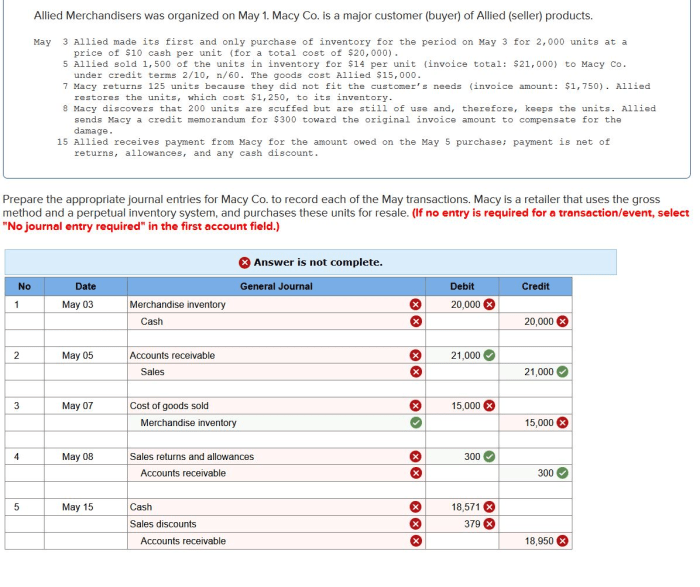
Upon receipt of an invoice, the accounts payable department initiates the processing procedures. The invoice is first checked for completeness and accuracy, including verifying the invoice number, date, vendor information, and purchase order details. Any discrepancies or missing information are promptly communicated to the vendor for clarification.
Invoice Approval Process
Once the invoice is verified, it is routed for approval to the appropriate department head or authorized signatory. The approver reviews the invoice to ensure that the goods or services have been received and accepted, and that the charges are in accordance with the agreed-upon terms and conditions.
The invoice approval process is typically completed within three to five business days, depending on the complexity of the invoice and the availability of the approver. In cases where additional documentation or verification is required, the approval process may take longer.
Payment Process
After the invoice has been approved, it is processed for payment. The accounts payable department issues a payment order to the vendor, which includes the invoice number, amount due, and payment terms. Payments are typically made within 30 days of invoice receipt, or in accordance with the agreed-upon payment terms.
Potential Delays or Bottlenecks
While the company strives to minimize delays in invoice processing, certain factors can contribute to potential bottlenecks:
- Incomplete or inaccurate invoices:Invoices that are missing information or contain errors may require additional follow-up with the vendor, leading to delays in processing.
- Unavailability of approvers:If the designated approver is unavailable due to vacation, illness, or other reasons, the invoice approval process may be delayed.
- Complex invoices:Invoices involving multiple line items, discounts, or other complex calculations may require additional time for review and verification.
- Vendor disputes:In cases where the company disputes the charges or the quality of goods or services received, the invoice payment may be delayed pending resolution of the dispute.
Payment Options and Considerations
The company has several payment options available for the invoice, each with its advantages and disadvantages. The choice of payment method should consider the impact on the company’s cash flow and vendor relationships.
Bank Transfer
Bank transfer is a secure and reliable method of payment. It is typically used for large payments or when the vendor is located in a different country. The main advantage of a bank transfer is that it provides a clear audit trail, making it easy to track the payment status.
However, bank transfers can take several days to process, which can be a disadvantage if the payment is time-sensitive. Additionally, bank transfers can incur fees, which can add to the cost of the payment.
Credit Card
Credit cards offer a convenient and flexible way to make payments. They are widely accepted by vendors and can be used for both online and offline payments. The main advantage of credit cards is that they allow the company to extend its payment terms, typically for a period of 30-60 days.
However, credit cards can also incur fees, which can be significant for large payments. Additionally, using credit cards can lead to debt if the balance is not paid in full each month.
PayPal
PayPal is an online payment service that allows companies to make payments securely and quickly. It is a popular option for online purchases and can also be used to make payments to vendors. The main advantage of PayPal is that it is easy to use and offers a high level of security.
However, PayPal can also incur fees, which can be a disadvantage for small payments. Additionally, PayPal may not be accepted by all vendors.
Vendor Communication and Negotiations
Effective communication and negotiation with vendors are crucial for managing invoice processing and ensuring timely payments. The vendor communication process involves establishing clear channels of communication and maintaining regular contact to address any queries or concerns.
Regular communication allows for prompt resolution of issues related to the invoice, such as discrepancies, errors, or payment delays. It also provides an opportunity to discuss ongoing negotiations or disputes related to the invoice. These negotiations may involve seeking discounts, payment extensions, or exploring alternative payment arrangements that are mutually beneficial.
Communication Channels
The communication channels used with the vendor can vary depending on the company’s preferences and the vendor’s availability. Common communication channels include:
- Phone calls
- Instant messaging (e.g., WhatsApp, Skype)
- Vendor portals
The choice of communication channel should consider factors such as the urgency of the matter, the level of detail required, and the vendor’s preferred mode of communication.
Negotiations, Company receives an invoice for 0
Ongoing negotiations or disputes related to the invoice may arise due to various reasons, such as discrepancies in the invoice amount, payment terms, or product/service quality. It is important to approach negotiations with a collaborative mindset and focus on finding mutually acceptable solutions.
When negotiating with the vendor, consider the following strategies:
- Clearly articulate the issue or concern.
- Provide supporting evidence or documentation.
- Be prepared to compromise and explore alternative solutions.
- Document the negotiations and agreements reached.
Discounts, Payment Extensions, and Alternative Arrangements
Negotiating discounts, payment extensions, or alternative payment arrangements can be beneficial for both parties involved. Discounts can reduce the overall cost of the invoice, while payment extensions can provide additional time to secure funds for payment.
Alternative payment arrangements, such as installment plans or barter agreements, may be explored when traditional payment methods are not feasible. It is important to evaluate the pros and cons of each arrangement carefully and ensure that it aligns with the company’s financial policies and cash flow.
Internal Reporting and Documentation
Internal reporting and documentation play a vital role in managing invoices effectively. Companies must establish clear internal reporting requirements to ensure that invoices are processed, recorded, and accounted for accurately.
Proper documentation and record-keeping are essential for maintaining an audit trail and providing evidence of transactions. This includes retaining invoices, payment records, and supporting documentation.
Accounting Software and Tools
To streamline invoice management, companies may consider utilizing accounting software or other tools. These tools can automate tasks such as invoice capture, data entry, approval workflows, and payment processing.
Compliance and Legal Considerations
Invoice processing and payment must adhere to relevant laws and regulations, ensuring ethical and legal compliance. Neglecting these requirements can lead to severe consequences.
Adhering to legal standards is crucial for maintaining business integrity, fostering trust with vendors, and mitigating risks. Failure to comply can result in legal penalties, reputational damage, and financial losses.
Applicable Laws and Regulations
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX):Enforces financial reporting accuracy and transparency, including invoice processing.
- Uniform Commercial Code (UCC):Governs commercial transactions, including invoice payment terms and dispute resolution.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS):Protects sensitive financial data during invoice processing and payment.
- Tax Laws:Determine invoice taxability, deductions, and reporting requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key elements of an invoice?
An invoice typically includes the invoice number, date, vendor information, customer information, line items (description of goods or services, quantity, unit price, and total price), payment terms, and any applicable taxes or discounts.
How should a company assess its financial standing before processing an invoice?
To assess its financial standing, a company should analyze its cash flow, profitability, and debt-to-equity ratio. This evaluation helps determine the company’s ability to pay the invoice and maintain financial stability.
What are some common payment options available for invoices?
Common payment options for invoices include bank transfers, checks, credit cards, and online payment platforms. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, such as processing time, fees, and security.